NewsDetails
Operation Manual for Plate and Frame Filter Press: A Full-Process Guide from Installation and Commissioning to Safe Operation
author:Shuangcheng time:2025-06-18 04:06:50 Click:198
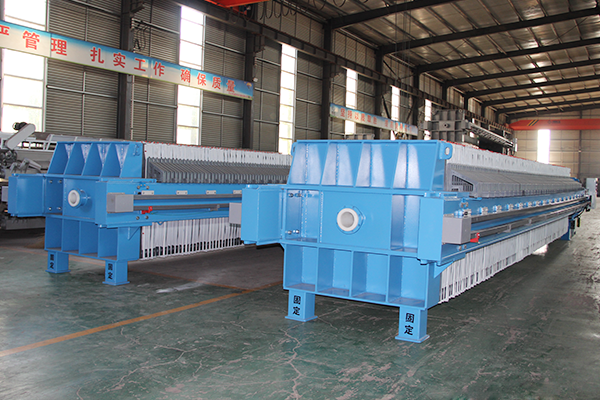
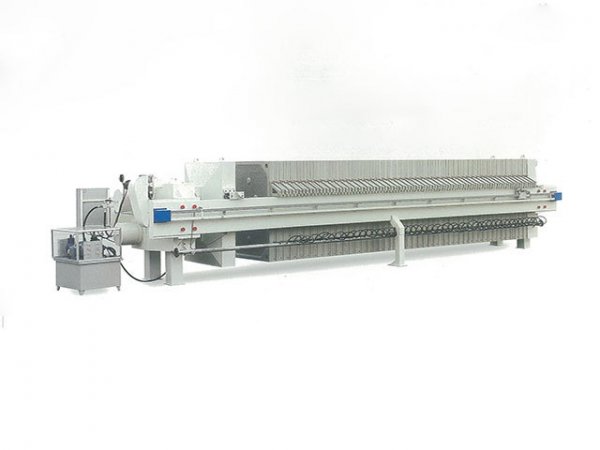
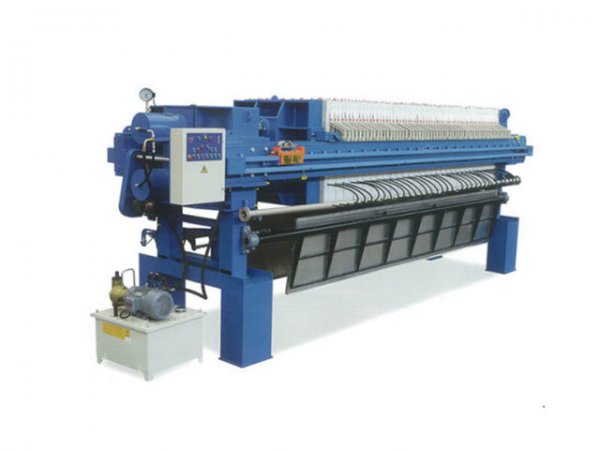
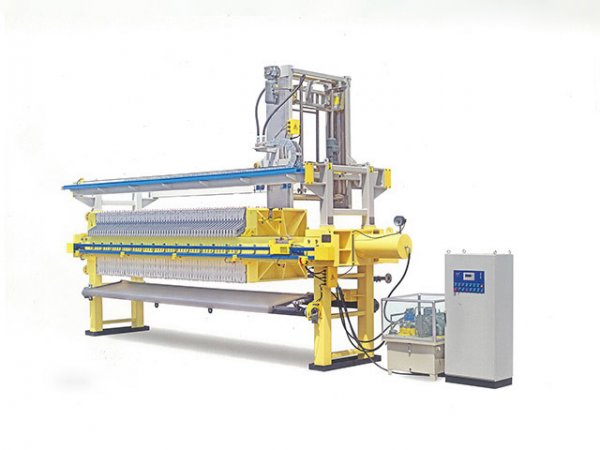
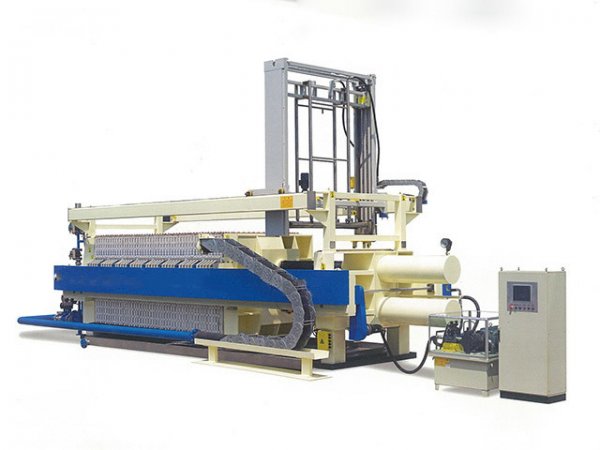
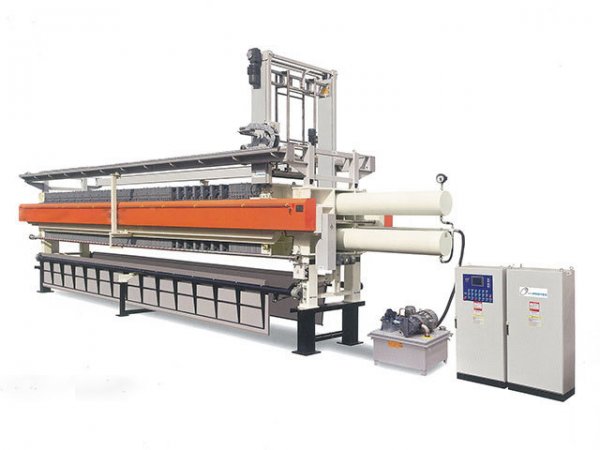
In the field of industrial solid-liquid separation, the Plate and Frame Filter Press has become a core piece of equipment in industries such as chemicals, mining, and wastewater treatment due to its efficient separation performance and flexible structural design. Standardized operation is crucial for ensuring the efficient operation of the equipment, extending its service life, and reducing safety risks. This document provides a comprehensive guide covering equipment installation, commissioning, operation, maintenance, and safety specifications.
I. Installation and Commissioning Process
(1) Pre-Installation Preparation
Site Requirements
Choose a well-ventilated and adequately lit site, ensuring sufficient operating space around the equipment (it is recommended to reserve more than 1.5 meters on all sides).
The ground must have sufficient load-bearing capacity (calculated in advance based on the equipment weight) and be level to avoid vibrations during operation.
Component Inventory Check
Cross-check the equipment list to ensure the completeness of components such as filter plates, filter frames, hydraulic system components, and electrical elements.
Inspect the appearance for any dents, deformations, or corrosion, ensuring no parts are missing or damaged.
Tools and Materials Preparation
Prepare installation tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and spirit levels, as well as materials like sealant, lubricating grease, and anchor bolts to ensure a smooth installation process.
(2) Installation Steps
Foundation Fixing
Lift the equipment to the designated location and use a spirit level to calibrate the machine's levelness.
Secure the equipment base to the ground using anchor bolts to prevent displacement or shaking during operation.
Component Assembly
Filter Plates and Frames: Arrange the filter plates and frames in order, ensuring smooth sliding of the guide rods. Cover the filter plates evenly with filter cloths, avoiding wrinkles or tears.
Hydraulic System: Install the hydraulic cylinder, oil pump, and piping, ensuring that hydraulic components are firmly connected and free from oil leakage risks.
Electrical System: Connect the motor, control box, and sensor wiring in accordance with electrical wiring specifications, labeling and protecting the wiring appropriately.
Piping Connection
Connect the feed pipe, filtrate discharge pipe, and hydraulic oil pipe, using sealant or sealing rings at the interfaces to ensure sealing performance and prevent material or hydraulic oil leakage.
(3) Commissioning Process
Hydraulic System Commissioning
Start the hydraulic pump and gradually increase the system pressure to the equipment's rated pressure.
Test the filter plate pressing and releasing functions, checking for oil leakage at piping connections.
Electrical System Commissioning
Power on the equipment and test the start/stop buttons of the control system, emergency stop button, and sensor signals (such as pressure sensors and liquid level sensors) for accuracy and sensitivity, ensuring the automation control function is normal.
No-Load Trial Run
Operate the equipment without material to observe the smooth movement of filter plates, check if the equipment noise is within the normal range, and ensure all components operate harmoniously without jamming.
Load Commissioning
Gradually add material for filtration testing, monitoring the filtration pressure, filtrate flow rate, and filter cake formation.
Adjust the feed speed and pressure to ensure the equipment operates stably within the design parameters.
II. Daily Operation Guidelines
(1) Pre-Startup Checks
Filter Cloths and Filter Plates: Confirm that the filter cloths are clean and undamaged, securely installed; ensure no material residue on the filter plate surfaces and no scratches or deformations on the sealing surfaces.
Hydraulic Oil and Lubricating Oil: Check the hydraulic oil level in the tank to ensure it is within the standard range and the oil quality is clear and free from impurities; supplement lubricating oil at lubrication points such as bearings and lead screws.
Electrical and Instrumentation: Check that the wiring connections are secure, and pressure gauges, sensors, and other instruments are zeroed and functioning normally.
(2) Operation Process Specifications
Feeding Stage
Slowly open the feed valve and control the feed speed to avoid filter cloth damage or filter plate displacement due to excessive impact.
Monitor the feed pressure to ensure it does not exceed the equipment's rated pressure.
Filtration Stage
Continuously monitor the filtration pressure and filtrate flow rate. When the pressure continues to rise and the filtrate flow rate significantly decreases, determine that the filter cake has basically formed and prepare for the pressing stage.
Pressing Stage
Set the pressing pressure and time according to the material properties (such as viscosity and moisture content). Gradually increase the pressure through the hydraulic system to further squeeze out moisture from the filter cake and improve solid content.
Discharge Stage
Release the filter plates in order and carefully remove the filter cake using a discharge device or manually, avoiding excessive pulling of the filter cloths.
Clean the filter cloths and filter plates promptly after discharge to remove residual material.
(3) Shutdown Operations
Normal Shutdown
Close the feed pump, slowly release the hydraulic system pressure, and sequentially shut down the motor and control box power.
Thoroughly clean the equipment to maintain its cleanliness.
Emergency Shutdown
In case of sudden leakage, abnormal vibration, or electrical failure, immediately press the emergency stop button, cut off the power supply, troubleshoot the issue, and only restart the equipment after repair.
III. Maintenance and Care Specifications
(1) Daily Maintenance
Cleaning Requirements: Rinse the filter cloths and filter plates immediately after each discharge. Conduct a thorough cleaning of the equipment surface and surrounding environment weekly to remove oil stains and material residues.
Fastener Inspection: Daily check the filter plate pressing bolts, anchor bolts, and other connecting parts, tightening any loose parts promptly.
Sealing Component Inspection: Observe sealing rings, gaskets, and other sealing components for signs of wear or aging, replacing any failed parts to prevent leakage.
(2) Regular Maintenance
Filter Cloth Replacement: Based on usage frequency and damage, it is recommended to inspect the filter cloth strength every 3-6 months. Replace the filter cloth if the damaged area exceeds a certain extent or if the filtration efficiency significantly decreases.
Hydraulic System Maintenance: Change the hydraulic oil every six months (the cycle may be shortened based on operating conditions) and clean the oil tank and piping. Annually inspect the sealing performance of hydraulic components and repair or replace worn parts.
Electrical System Maintenance: Annually check the insulation layer of wiring for aging, test the functionality of control components (such as relays and contactors) to ensure the electrical system is safe and reliable.
(3) Special Scenario Maintenance
Long-Term Shutdown: Before shutdown, thoroughly clean the equipment, keep the filter cloths and filter plates dry, apply anti-rust grease to hydraulic components and metal parts, cover with a dust cover, and power on the equipment for a trial run every quarter.
Post-Extreme Operating Conditions: After operation in high-temperature, low-temperature, or highly corrosive environments, increase the inspection frequency of sealing components, filter cloths, and metal structures, and conduct anti-corrosion treatment or component upgrades as necessary.
IV. Safe Operation Guidelines
(1) Operator Requirements
Training and Assessment: Operators must undergo professional training and pass an assessment, familiarizing themselves with the equipment principles, operating procedures, and safety precautions, and obtaining certification before taking up the post .
Protective Equipment: During operation, operators must wear protective gloves, safety goggles, and work clothes to prevent material contact with the skin or splashing into the eyes.
(2) Risk Prevention Measures
Pressure Overload Protection: Install a safety relief valve and calibrate it regularly to ensure automatic pressure relief when the system pressure exceeds the rated value, preventing equipment bursting.
Electrical Safety: The equipment must be reliably grounded, and wiring must be protected in conduits to prevent moisture or rodent damage. Regularly check the grounding resistance and wiring insulation performance.
Mechanical Injury Prevention: Install protective barriers around moving parts (such as filter plate sliding rails and hydraulic piston rods). Regularly test the emergency stop device to ensure its sensitivity.
(3) Emergency Response Procedures
Leakage Accidents: Immediately shut down the equipment, cut off the feed source, use sandbags or absorbent materials to block the leakage point, clean up the material, inspect the sealing components or piping, and only restart after repair.
Electrical Failure: Quickly cut off the power supply and have a professional electrician troubleshoot the issue. Non-professional personnel are prohibited from conducting repairs.
Personal Injury: In case of material burns or mechanical crushing, immediately stop the equipment, clean or dress the injured area, and seek medical attention promptly.
V. Common Issues and Solutions
(1) Decreased Filtration Efficiency
Possible Causes: Clogged filter cloth, insufficient feed pressure, poor filter plate sealing.
Solutions: Clean/replace the filter cloth, adjust the feed pressure, inspect the sealing components.
(2) Abnormal Equipment Vibration
Possible Causes: Uneven filter plate installation, loose anchor bolts, worn bearings.
Solutions: Readjust the filter plates, tighten the bolts, replace the bearings.
(3) Hydraulic System Failure
Possible Causes: Contaminated hydraulic oil, piping leakage, hydraulic pump failure.
Solutions: Replace the hydraulic oil, repair the piping, overhaul/replace the hydraulic pump.
VI. Conclusion
Standardized operation is the core of the stable operation of the Plate and Frame Filter Press. From precise positioning during installation and commissioning to standardized daily operation procedures and meticulous maintenance and safety controls, each step must strictly adhere to technical requirements. By continuously optimizing operational habits and maintenance strategies, not only can equipment efficiency be improved, but also a foundation can be laid for production safety and sustainable development. It is recommended that enterprises establish operation logs, regularly review equipment operation data, continuously improve operational procedures, and maximize the value of the equipment.
 Recommended Products
Recommended Products
 Contact us
Contact us
—— Contact:Manager
—— Tel:+86 16632826789
—— Email:sales@hbscfilterpress.com
—— Url:https://www.hbscfilterpress.com
—— Address:West Zone of Economic Development Zone, Fucheng County, Hengshui City, Hebei Province